Showing posts with label remote. Show all posts
Showing posts with label remote. Show all posts
Sunday, September 21, 2014
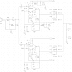
Remote Field Strength Meter Circuit Diagram
Remote Field Strength Meter Circuit Diagram. This field strength meter consists of a tuned crystal detector producing a dc output voltage from a transmitted signal. The dc voltage is used to shift the frequency of a transmitter of 100-mW power operating at 1650 kHz. The frequency shift is proportional to the received field strength. This unit has a range of several hundred feet and is operated under FCC part 15 rules (100-mW max power into a 2-m-iong antenna between 510 and 1705 kHz).
Remote Field Strength Meter Circuit Diagram

Wednesday, May 1, 2013
Remote Controlled Surveillance Robot
This post will provide you with the basic information on how a remote controlled vehicle can be constructed. Read on to know more about this.

- 1.2Ghz 1000mW Receiver+Transmitter
- USPS Priority Mail boxes
- Hitec Optima 6 2.4Ghz Receiver
- Arrowind 18A Brushless Speed Controller
- 2200mAh 20C LiPo Battery Pack
- Brushless motor
- Custom motor-reversing relay board
- Foam wheels
- 7-Inch Handheld LCD TV
- Servo
The first thing to do here is to test the wireless transmitter. All the required components are mounted on the USPS mail box. Once the test is done, the box is strapped onto a nitro RC truck. The vibrations caused prevents the truck to be driven via the wireless video feed. The best thing to do in this case is to add wheels and propulsion to the box.
Labels:
controlled,
remote,
robot,
surveillance
Friday, April 12, 2013
Infra Red Remote Control Tester
This little circuit is invaluable for quick go/no-go testing of just about any remote control transmitting infra-red (IR) light. The tester is battery-powered, built from just a handful of commonly available and inexpensive parts, and fits in a compact enclosure. Schmitt trigger gate IC1f is used as a quasi-analogue amplifier with, unusually, an infra-red emitting diode (IRED) type LD274 acting as the sensor element. An R-C network, C1-R2, is used at the output of the gate because all IR remote controls transmit pulse bursts, and to prevent the output LED, D2, lighting constantly when day-light or another continuous source of IR light is detected.
 Circuit diagram:
Circuit diagram:


 Cased project:
Cased project:
 This creates a useful ‘quick test’ option: point the tester at direct daylight, and the indicator LED should light briefly. The sensitivity of the tester is such that IR light from remote control is detected at a distance of up to 50 cm. The circuit is designed for very low power consumption, drawing less than 1 mA from the battery when IR light is detected, and practically no current when no light is detected. Hence no on/off switch is required. The construction drawing shows how the tester may be ‘cased’ using a small ABS case from Conrad.
This creates a useful ‘quick test’ option: point the tester at direct daylight, and the indicator LED should light briefly. The sensitivity of the tester is such that IR light from remote control is detected at a distance of up to 50 cm. The circuit is designed for very low power consumption, drawing less than 1 mA from the battery when IR light is detected, and practically no current when no light is detected. Hence no on/off switch is required. The construction drawing shows how the tester may be ‘cased’ using a small ABS case from Conrad.
COMPONENTS LIST
Resistors:
R1,R2 = 10MW
Capacitor:
C1 = 10nF
Semiconductors:
D1 = LD274 (Siemens)
D2 = LED, 3mm, low-current
IC1 = 74HC14
Miscellaneous:
Bt1 = 3V Lithium cell with solder tags, e.g.type CR2045 (560 mAh)
Read More..
 Circuit diagram:
Circuit diagram:COMPONENTS LIST
Resistors:
R1,R2 = 10MW
Capacitor:
C1 = 10nF
Semiconductors:
D1 = LD274 (Siemens)
D2 = LED, 3mm, low-current
IC1 = 74HC14
Miscellaneous:
Bt1 = 3V Lithium cell with solder tags, e.g.type CR2045 (560 mAh)
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)